Evading IDS, Firewalls, and Honeypots
IDS Firewalls and Honeypot concepts
Intrusion detection system
- inspects inbound and outbound traffic for suspicious activity
- Checks traffic for signatures and patterns and alarms when a match is found
- IDS can be place outside of inside a firewall
- Before deploying an IDS it is important to understand how information flows through the network
- Signature Recognition – Tries to identify events that are the miss uses of network resources
- Anomaly Detection – detects intrusions based on fixed behaviors of the users or components in a system
- Protocol Anomaly Detection – Explores anomalies in the way vendors deploy the tcp/ip specification
General Indication of Intrusions
- File System Intrusions
- New unfamiliar files or programs
- Change of file permissions
- Unexplained change in file size
- Rouge files on the system that do not correspond to the master list of singed files
- Missing files
- Network Intrusions
- Repeated probes of available services on machines
- Connections from unusual locations
- Repeated login attempts to remote host
- Sudden influx of log data
- System Intrusions
- Short of incomplete logs
- Unusually slow system
- Missing logs or logs with incorrect permissions
- Modifications to system software and config files
- Unusual guis or text messages
- Gaps in system accounting
- System crashes or reboots
- Unfamiliar processes
Types of IDS
- Network based intrusion detection systems
- Runs in promiscuous mode and listens for patterns of indicative of an intrusion
- Detects activity like DoS, port scans, or attempts to crack into computers by watching network traffic
- Host base intrusion detection systems
- Audits for events that occur on specific host
- Not as commons due to overhead of monitoring each system event
- LFM IDS
- Monitors log files and watches for strange activity
- File integrity checking
- Watches file and makes sure they are not modified
IDS Alerts
- True positive – legitimate attack
- False positive – no attack
- False negative – legitimate attack that was not alerted on
- True negative - IDS does not raise an alarm when an attack has not taken place
Firewall
- Hardware or software designed to prevent unauthorized access
- Placed at a junction or gateway
-
Examines all messages entering or leaving the intranet
- Firewall Architecture
- Bastion Host
- Designed and configure to protect network resources from attacks
- Has two interfaces public or private
- Screened subnet
- DMZ
- Contains hosts that offer public services
- Responds to public requests and has no hosts accessed by private network
- Private zone cannot be accessed by internet users
- Multi-homed firewall
- Firewall has two or more interfaces that allows further subdivision
- Specific security objectives
- Bastion Host
- DeMilitarized Zone (DMZ)
- DMZ is a network that serves as a buffer between the internal secure network and insecure internet
- Created using a firewall with three or more network interfaces
- Is an untrusted network were servers that are access by the public and be connected to by host on the internet
- Types of firewalls
- Hardware firewall
- A dedicated stand alone device
- Filters network traffic using packet filtering
- Used to filter out the network traffic of large business networks
- Has increased level of security controls
- Faster speed
- Minimal interference
- More expensive
- Hard to implement and configure an requires more space
- Software Firewall
- A firewall software program installed on a computer just like normal software
- Used to filter traffic for individual home users
- Only filters traffic for the computer on which it is installed
- Less expensive than hardware firewalls
- Ideal for personal or home use
- Easier to configure and reconfigure
- Consumer host resources
- Difficult to uninstall
- Not appropriate for environments requiring faster response times
- Hardware firewall
-
Firewall Tech
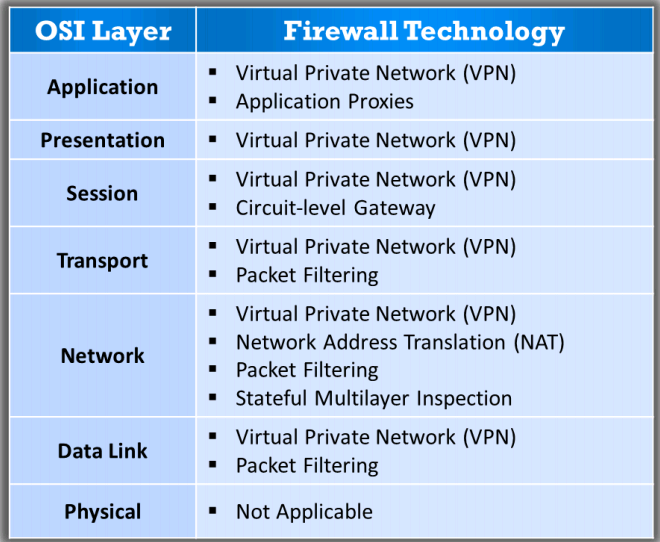

- Packet Filtering Firewall
- Packet filtering firewalls work at the network layer and are usually part of a router
- Each packet is compared to a set of criteria before being forwarded
- Depending on the packet and the criteria the firewall will drop or forward the packet
- Rules can included source and destination ip address, the source and the destination port number, the protocol used, TCP flag bits, direction, or interface
- Circuit-Level Gateway firewall
- Session layer firewall / TCP layer
- Information passed to a remote computer through a circuit level gateway appears to have originated from the gateway
- They monitor requests to create sessions and then determine if those sessions are allowed
- Circuit proxy firewalls allow or prevent data streams
- THEY DO NOT FILTER INDIVIDUAL PACKETS!!
- Application level firewall
- Application level gateways (proxies) can filter packets at the application layer
- Incoming and outgoing traffic is restricted to services supported by proxy all other service requests are denied
- Application-level gateways configured as a web proxy prohibit FTP, gopher, telnet, or other traffic
- Examine traffic and filter on application specific commands such as http post
- Active application level firewalls - examine all incoming request and will only allow genuine request through
- Passive application level firewalls – Work like IDS they check all incoming request by do not allow or deny just log the information
- Stateful multilayer inspection firewall
- Combine the aspects of three types of firewalls
- Packet filtering
- Circuit level
- Application level
- They filter packets and the network layer to determine if a session packet is legitimate and they evelauate the contents of the packet at the application layer
- Combine the aspects of three types of firewalls
Application Proxy
- Filters connections for specific services
- Act as proxy servers
- Filter connections based on services and protocols
- Example an ftp proxy will only allow ftp traffic to pass through
- Advantages
- Can be good at logging because they understand the application layer
- Proxy services reduce the load on the network links as they are capable of cahing information
- Perform user level authentication
- Automatically protect weak or faulty ip implementations
- Disadvantages
- Proxy services lag behind non proxy services until suitable proxy software is available
- Each service in a proxy may use different servers
- Proxy services may require changes in the client, application, and procedures
Network Address Translation (NAT)
- Separates IP address into two sets
- Allows LAN devices to use WAN IP addresses
- NAT modifies the packets the router sends
- Has the ability to change the address of a packet and make it appear to have arrived from a valid address
- It limits the number of public IP address and organization can use
- It can act as a firewall filtering technique where it allows only those connections which originate on the inside network and will block connections which originate on the outside network
- Advantages
- NAT helps enforce firewall control over outbound connections
- Restricts incoming traffic and allows only packets that are part of a current interaction initiated from the inside
- Disadvantage
- NAT has to guess how long to keep a translation
- NAT interferes with encryption and authentication services
- Dynamic allocation of ports may interfere with packet filtering
Virtual Private Network (VPN)
- Private network constructed using public networks
- Used to secure transmission of sensitive information over an untrusted network using encapsulation and encryption
- Establishes a virtual point to point connection through use of dedicated connections
- Only devices running the VPN software can access the VPN
Firewall Limitations

Honeypot
- Setup to attract and trap people whe attempt to penetrate an organizations network
- Does not have any production value
- Any traffic to it is likely to probe attack or compromise
- Can log port access attempts
- Monitor attackers keystrokes
- Can be used for early warning signs
- Types of fHoneypots
- Low Interaction Honeypots
- Simulate only a limited number of services and applications of a target system or network
- Set to collect higher level information about attack vectors such as network probes and worm activities
- Medium Interaction Honeypots
- Simulate a real operating system applications and its services
- Can respond to pre configured commands therefor risk of intrusion is increased
- High interaction Honeypots
- Simulates all services
- Captures complete information about an attack vector such as attack techniques tools and intent of the attack
- Production Honeypots
- Emulate real production networks
- Set to collect internal flaws and attackers within an organization
- Research Honeypots
- These are high interaction honeypots primarily deployed in research institutes government or milita+ry organizations
- Capture in depth information about the way an attack is performed vulnerabilities exploited and the attack techniques used by the attacker
- Low Interaction Honeypots
IDS Firewall and Honeypot Solutions
Snort
- Open source network IDS performs real time traffic analysis and packet loggin on IP networks
- Performs protocol analysis and content searching / matching
- Used to detect a variety of attacks and probes
-
Uses flexible rules language to describe traffic it should collect or pass as well as a detection engine that utilizes a modular plugin architecture
- Uses of snort
- Straight packer sniffer like TCP dump
- Packet logger
- Network IPS
- Snort Rules
- Enables custom rules to meet the needs of networks
- Help different between normal internet activities and malicious activities
- Must be contained in a single line snort does not handle rules on multiple lines
- Snort rules have two parts
- Rule header and rule options
- Snort Rules Actions and IP Protocols
- Rule header stores the complete set of rules to identify the packet and determine the action that is being performed
- The rule action alerts snort when it finds a packet the matches the rule
- Three actions snort can take
- Alert – Generates an alert using the selected alert method and then logs the packet
- Log– Logs the packet
- Pass – drops / ignores the packet
- Three IP protocols available for snort
- TCP
- UDP
- ICMP
- Snort Rules Detection Operator and IP Address
- Direction operator indicates the direction of interest for the traffic
- Traffic can flow in either single or bidirectional
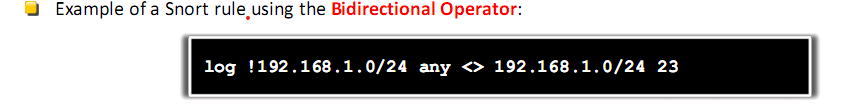
- Use keyword any to identify any IP address
- Use CIDR notation
- Snort Rules Port Numbers
- Can be listed with Any static port port range and by negation
- Range operator is :
IDS Tipping Point
- In line threat protection software
- Does not affect performance and productivity
AlientVault
- OpenSource SIEM
- Normalization and correlation
- Advance threat detection
KFSensor
- Host Based IDS that acts as a Honeypot to attract the detection hacker and worms simulates vulnerable system services and trojan
Specter
- Honeypot based on IDS
- Offers common internet services
Evading IDS
Techniques
Insertion Attack
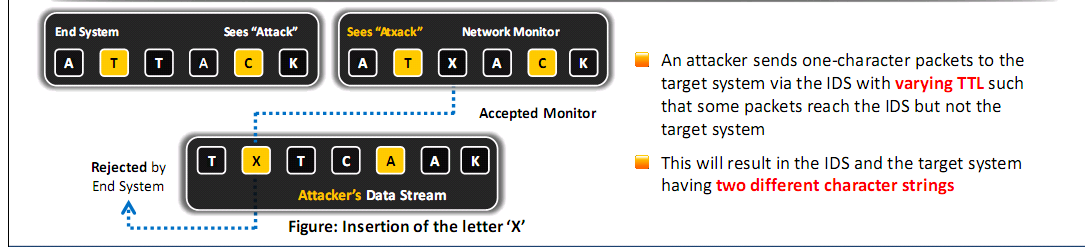
- Attacker confuses the IDS by forcing it to read invalid packets
- An IDS blindly believes and accepts a packet that an end system rejects and the attacker exploits this condition and inserts data into the IDS
- Occurs when NIDS is less strict in processing packets than the internal network
- The attacker obscures extra traffic and IDS concludes the traffic is harmless
- The IDS gets more packets than the destination
- IDS and the end system construct two different strings
Evasion
- End System Accepts a packet that an IDS rejects
- Using this technique an attacker exploits the host computer without the IDS ever realizing it
- Attacker sends portions of the request in packet that the IDS mistakenly rejects allowing the removal of parts of the stream from the IDS
- The IDS gets fewer packets than the destination
DoS
- IDSs use a centralized server for logging alerts
- If attackers know the IP address of the centralized server they can perform a DoS or other hack to slow down or crash the server
- As result attacker intrusion attempts will not be logged
Obfuscation
- Encode the attack packet payload
- Attackers manipulate the path referenced in the signature to fool the HIDS
- Attackers can encode attack patterns in Unicode to bypass IDS filtering but be understood by an iis webserver
- Polymorphic code is another means to circumvent signature based IDS by creating unique attack patterns
- Use encrypted protocols such as https so the IDS cant read the packet
False Positive Generation
- Craft malicious packets just to generate alerts
- These packets generate a large number of false positive alerts
- False positives are used to hide the real attack traffic
- Makes it difficult to differentiate the attack traffic with the false positives
Session Splicing
- Attacker splits the attack traffic into many packets
- It is effective against IDS that do not reconstruct packets before checking them against intrusion signatures
- If attackers are aware of delay in packet reassembly at the IDS the can add delay between packet transmissions to bypass the reassembly
- IDS stops reassembly if they do not receive packets within a certain time
- IDS will stop working if the target host keeps session active for a time longer than the IDS reassembly time
- Any attack attempt after a successful splicing attack will not be logged by the IDS
Unicode Evasion
- Unicode is a character coding system to support worldwide interchange processing and display of the written texts
- In the Unicode space all the code points are treated differently but it is possible that there could be multiple representations of a single character
- Because of this complexity some IDS handle Unicode improperly
- Attacker convert attack string into Unicode to avoid IDS
Fragmentation Attack
- Can be used when fragmentation timeouts vary between IDS and host
- If a fragment reassembly timeout is 10 sec at the IDS and 20 sec at the target system attackers will send the second fragment after 15 secs
- IDS will drop the fragment as the second fragment is received but the target will reassemble the fragment
- When and IDS timeout exceeds the Victims timeout multiple fragments can be sent at different times so that the IDS receives some packets and the target receives other
Overlapping Fragments
- Generates a series of tiny fragments with overlapping TCP sequence numbers
Time to live
- Attacker needs to have prior knowledge of the topology
- This information can be obtained using tools such as traceroute
- IDS will receive both fragments target receives first fragment only
Invalid RST packet
- Attacker send RST packet to the IDS with an Invalid checksum
- IDS stops processing the packet thinking the TCP communication session has ended
- The target checks the RST packet checksum and drops it because it is invalid
Urgency Flag
- IDS do not consider the urgent pointer
- This results in the IDS and the target systems having different sets of packets
Polymorphic Shellcode
- Signature based NIDS identifies an attack by matching attack signatures with incoming and outgoing data
- Signatures are based off of commonly used string in shell code
- Polymorphic shellcode includes multiple signatures making it difficult to detect the signature
- Encode the payload using some technique and then place a decoder before the payload
- Shellcode is completely rewritten each time is is sent evading detection
- This technique also evades the commonly used shellcode strings
ASCII Shellcode
- ASCII Shellcode can be used to evade IDS because the pattern matching does not work with the ASCII values
- Scope of ASCII shellcode is limited as all assembly instructions cannot be converted to ASCII values directly
- Can be overcame by using other sets of instructions for converting ASCII values properly
Application Layer Attacks
- Uses compression to had malicious code
- Signature IDS cannot detect signature in compressed files
- Enables an attacker to exploit the vulnerabilities in compressed data
Desynchronization
- Pre Connection SYN
- Initial SYN packet is sent before the real connection
- If the SYN packet is received after the TCP control block is opened the IDS resets the appropriate sequence number to match that of the newly received SYN packet
- Attackers send fake SYN packets with a completely invalid sequence number to desync the IDS
- Stops the IDS from monitoring all legit traffic
- Post Connection SYN
- Attempts to desync the IDS from the actual sequence numbers that the kernel is honoring
- Send a post connection SYN packet in the data stream whish have divergent sequence numbers
- Target ignores the SYN packet as it references an already established connection
- The point of the attack is to get the IDS to resync its notion of the sequence numbers to the new SYN packet
- Causes the IDS to ignore legitimate part of the original stream
- Once the IDS resyncs a RST packet is sent to close down the connection
Encryption
- Encrypted sessions with the victim cant be read by the IDS
Flooding
- Attacker sends loads of unnecessary traffic to produce noise
Evading Firewalls

Firewall Identification
- Port Scanning
- Identifies open ports and services running
- Open ports can be further probed to identify the version of services
- Some firewall will uniquely identify themselves with how they respond to simple port scans
- Firewalking
- Uses TTL values to determine gateway ACL filters and map networks by analyzing ip packet responses
- Attacker sends TCP or UDP packet to the targeted firewall with aTTL set to on hop greater than the firewall
- If the packet makes it through the firewall a TTL exceeded in transit will be returned
- Banner Grabbing
- Banners announce the service that is running on the port
- Banner grabbing is a fingerprint method
- Main services that send out banners are FTP telnet and web servers
IP Address Spoofing
- IP Address spoofing is a hijack technique in which an attacker masquerades as a trusted host to conceal his identity spoof web sites hijack browsers or gain unauthorized access to a network
- Attackers modify the addressing information in the IP packet header and the source address bits field in order to bypass the firewall
Source Routing
- Allows the sender of a packer to specify the route the packet takes through the network
- As the packet travels through the nodes in the network each router examines the destination IP address and chooses the next hop to direct the packet to the destination
- In source routing the sender makes some of these decisions
- Allows the attacker to avoid going through the firewall
Tiny Fragments
- Attacker creates tiny packet fragments forcing some of the TCP packet header information into the next fragment
- IDS filter rules that specify patterns will not match with the fragmented packets due to broken header information
- The attack will succeed if the filtering router examines only the first fragment and allows other fragments to pass through
- This attack is used to avoid user defined filtering rules and works when the firewall checks only for the tcp header information
Bypass Blocked Sites using IP address in Place of URL
- This method involves typing the IP address directly in browsers address bar in place of typing the blocked website domain name
Bypass blocked sites using anonymous website surfing
- Uses VPN or proxy to encrypt traffic
Bypassing firewall through ICMP tunneling method
- Allows tunneling a backdoor shell in the data portion of ICMP echo packets
- The payload portion of an ICMP packet is not examined by many firewalls
Bypassing firewall through ACK tunneling Method
- Tunneling a backdoor application with TCP packets with ACK bit set
- ACK bit is used to acknowledge receipt of a packet
Bypassing Firewall through HTTP tunneling Method
- HTTP tunneling allow attackers to tunnel data through HTTP packets
- HTTP tunneling allow sending traffic for other services like FTP over HTTP or HTTPS
Bypassing firewall through SSH tunneling
- Attackers use openssh to encrypt and tunnel all the traffic from a local machine to a remote machine to avoid detection by perimeter security controls
Bypassing firewall through external systems
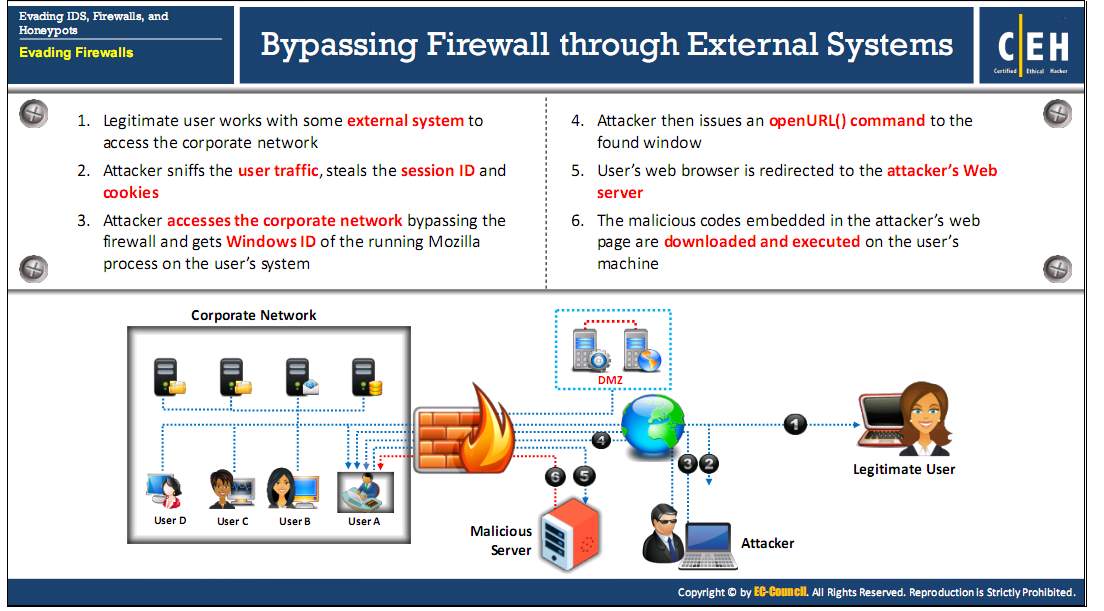
Bypassing firewall through MITM attack
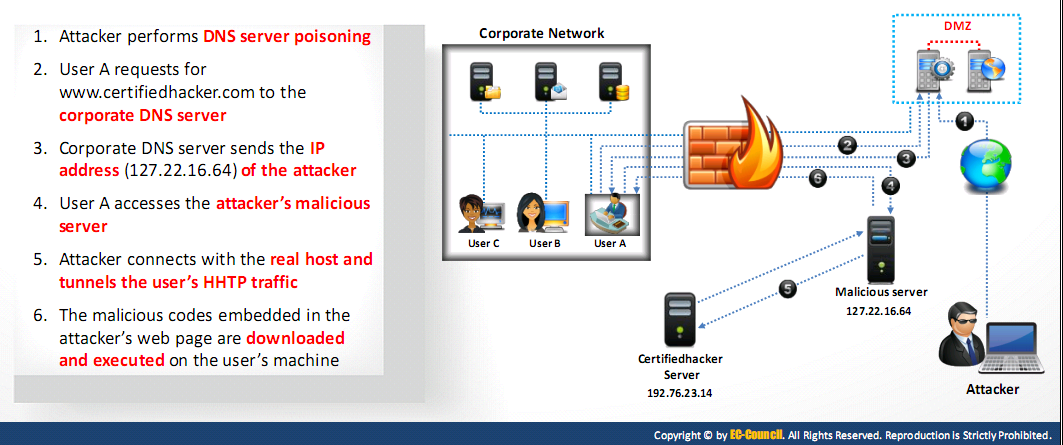
- Attackers make use of the DNS server and routing techniques to bypass restrictions
Bypassing through content
- Attacker sends the content containing malicious code to the user and tricks him/her to open it so that the malicious code can be executed
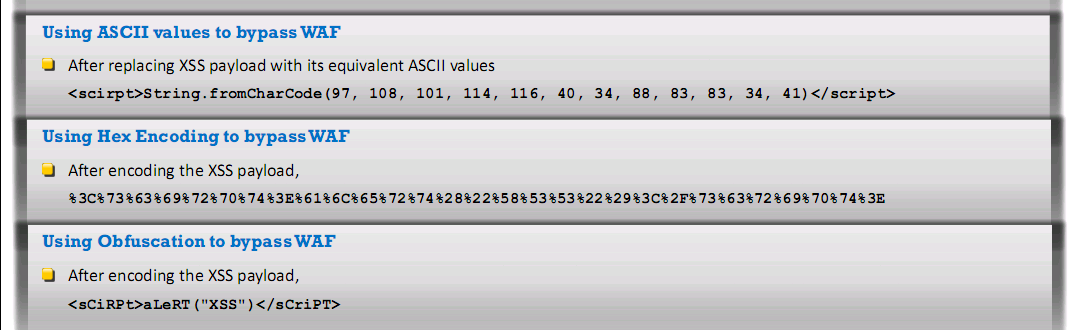
Bypassing Web application firewall (WAF) using XSS attack
- XSS attack exploits vulnerabilities that occur while processing input parameters of the end users and the server responses in a web application
- Attackers inject malicious HTML code in the victims website to bypass the WAF
IDS/Firewall Evading Tools
Traffic IQ Professional
- Enables security professionals to audit and validate the behavior of security devices by generating the standard application traffic or attack traffic between two virtual machines
Colasoft Packet builder
- Network packet crafter
- Used to build all types of custom networks
Detecting Honeypots
- Attacker can determine the presence of honeypots by probing the services running on a system
- Attackers craft malicious probe packets to scan for services such as HTTPS SMTPS and IMAPS
- Ports that show a particular service running but deny a three way handshake connection indicated the presence of a honeypot
Detecting and Defeating Honeypots
- Detecting presence of Layer 7 Tar Pits
- Look at the latency of the response from the service
- Detecting presence of layer 4 tar pits
- Analyze the TCP window size where tar pits continuously acknowledge incoming packets even though the TCP window size is reduced to zero
- Detecting presence of layer 2 tar pits
- Look for the response with unique MAC address which act as kind of black hole
- Need to be on the same layer 2 network
- Detecting Honeypots running on VMWare
- Look at the IEE standards for the current range of MAC addresses assigned to VMWare Inc
- Detecting presence of Honeyd Honeypot
- Perform time based TCP finger printing methods
- Detecting presence of user mode linux honeypot
- Analyze the files such as /proc/mounts /proc/interrupts and /proc/cmdline
- Detecting presence of Sebek based honeypots
- Sebek logs everything that is accessed via read() before transferring to the network causing congesting effect Analyze congestion in the network layer
- Detecting presence of snort inline honeypot
- Analyze outgoing packets by capturing Snort_inline modified packet through another host system and identifying the packet modification
- Detecting presence of fake AP
- Fake access points only send beacon frames but do not generate any fake traffic on the access points and an attacker can monitor the network traffic and easily notice the presence of fake AP
- Detecting presence of bait and switch honeypots
- Look at specific TCP/IP parameters like round trip time, TTL, and the TCP timestamp
Send Safe Honeypot Hunter
- Look at specific TCP/IP parameters like round trip time, TTL, and the TCP timestamp
- Tool designed for checking lists of HTTPS and SOCKS proxies for Honey pots
IDS Firewall Evasion Countermeasures
How to defend Against IDS Evasion
- Shutdown switch ports
- Perform in depth analysis of ambiguous network traffic
- Use TCP FIN or RST packet to terminate malicious TCP sessions
- Look for code other than 0x90 to defend against polymorphic shellcode
- Train users to identify attack patterns and regularly update/ patch
- Deploy IDS after a through analysis of network topology nature of network traffic and the number of host to monitor
- Use a traffic normalizer to remove potential ambiguity from packet stream before it reaches IDS
- Ensure IDS normalize fragmented packets and allows those packets to be reassembled In the proper order
- Define DNS server for client resolver in routers or similar network devices
- Harden the security of all communication devices such as modems, routers, switches, etc
- Block ICMP TTL expired packets
- Update antivirus signature regularly
- Use a traffic normalization solution at the IDS to prevent the system against evasion
- Store the attack information for future analysis
How to defend against firewall evasion

Firewall Penetration Testing
Firewall IDS Penetration Testing
- Helps evaluate ingress and egress traffic filtering capabilities
