Hacking Mobile Platforms
Mobile Platform Attack Vectors
OWASP Top 10 Mobile Risks
- M1 - Improper Platform Usage - misuse of features or security controls (Android intents, TouchID, Keychain)
- M2 - Insecure Data Storage - improperly stored data and data leakage
- M3 - Insecure Communication - poor handshaking, incorrect SSL, clear-text communication
- M4 - Insecure Authentication - authenticating end user or bad session management
- M5 - Insufficient Cryptography - code that applies cryptography to an asset, but is insufficient (does NOT include SSL/TLS)
- M6 - Insecure Authorization - failures in authorization (access rights)
- M7 - Client Code Quality - catchall for code-level implementation problems
- M8 - Code Tampering - binary patching, resource modification, dynamic memory modification
- M9 - Reverse Engineering - reversing core binaries to find problems and exploits
- M10 - Extraneous Functionality - catchall for backdoors that were inadvertently placed by coders
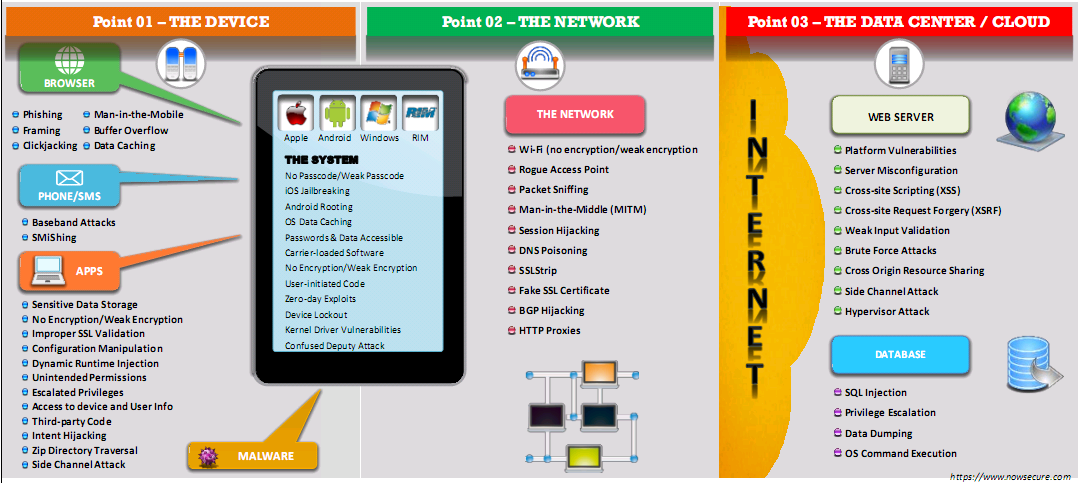
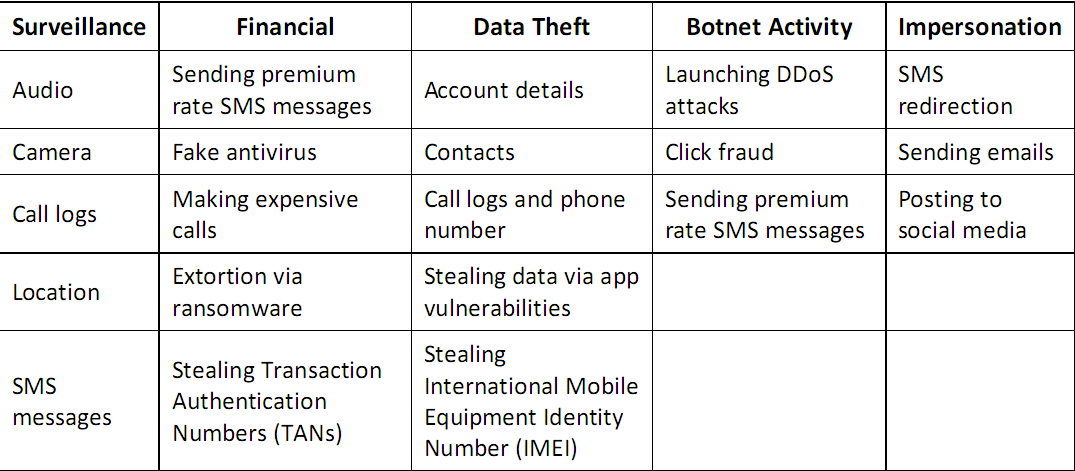
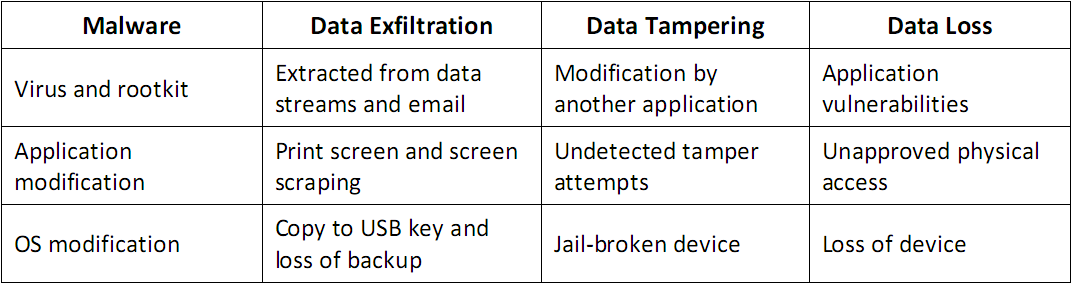
Anatomy of a Mobile Attack
Hackers Profit
Mobile Attack Vectors
Platform Vulnerabilities and Risk
- Malicious app in stores
- No vetting of apps
- Mobile Application vulnerabilities
- Mobile Malware
- Privacy Issues (Geolocation)
- App sandboxing vulnerabilities
- Protects systems and users by limiting the resources that the app can access to the mobile platform
- Weak data security
- Weak device and app encryption
- Excessive Permissions
- OS and app updates’ issues
- Weak Communication security
- Jailbreaking and rooting
- Physical attacks
- Mobile Spam
- Unsolicited text/email messages sent to mobile devices
- Can contain ads or malicious links
- SMS Phishing Attack
- Acquire personal and financial information by sending SMS
- Acts the same as a phishing attack but instead uses SMS
- Pairing to Open Bluetooth and Wi-Fi Connections
- Allows for eavesdrop and interception of data transmission
- Bluesnarfing and Bluebugging
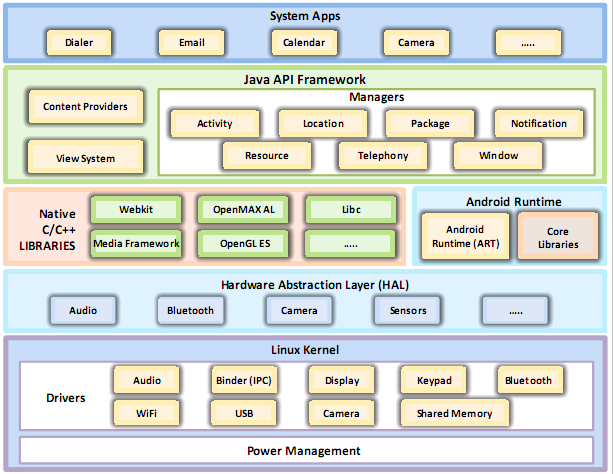
Hacking Android OS
- Android OS Basic Info
- Developed by google
- Features
- Enabling reuse and replacement of components
- Variety of pre-build UI components
- Open source Blink and Webkit engine
- Media Support
- Rich development enviorment
- Android Device Administration API
- Allows for security-aware apps that may help IT professionals
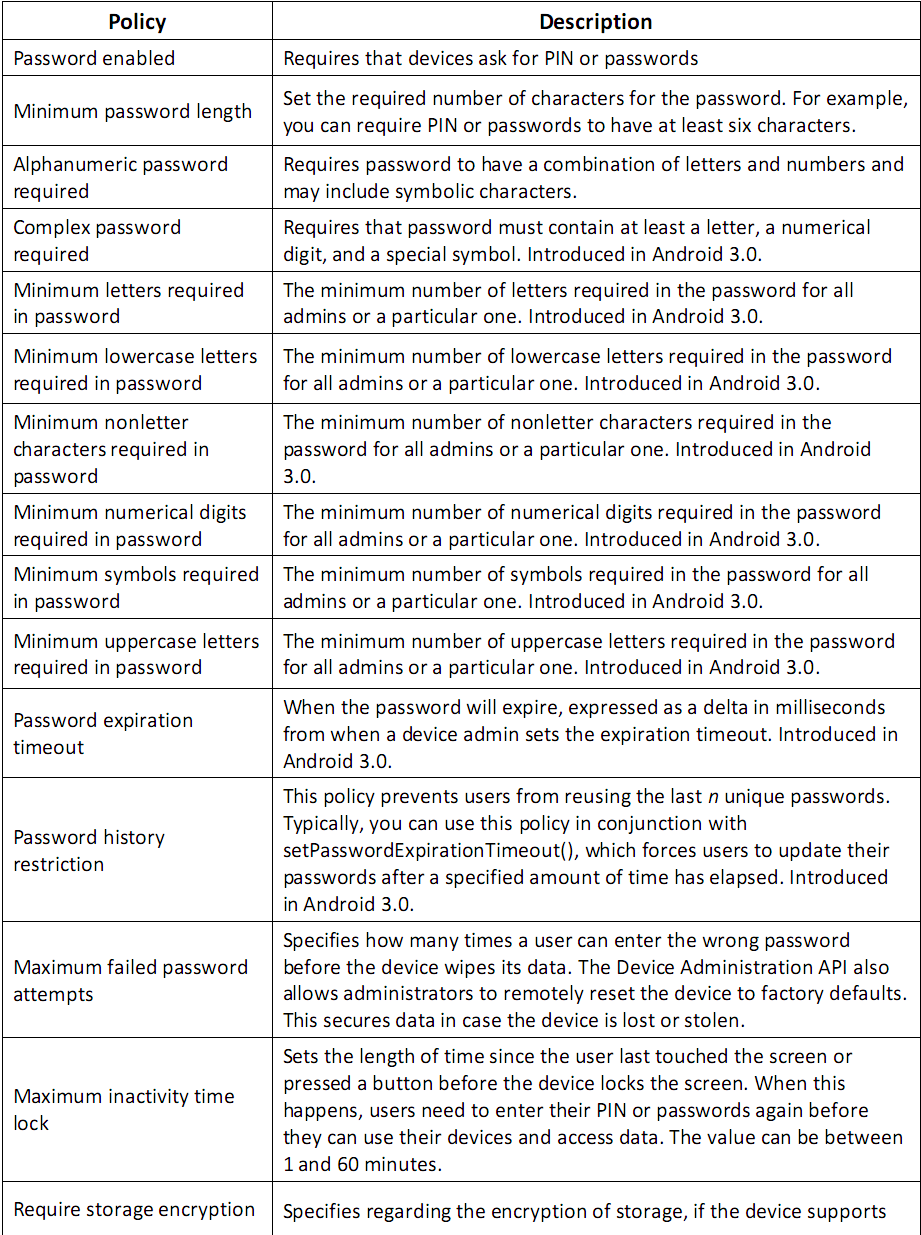

- Allows for security-aware apps that may help IT professionals
- Android Rooting
- Allows user to attain privileged control within androids subsystem
- Involves executing security vulnerabilities in the device firmware and granting execute permissions
- Rooting Tool
- KingoRoot - can be used with or without a PC
- TunesGo - Root Android - Done with PC
- One Click Root - Done with PC
- Android Attack Tools
- NetCut - Wifi killing application; blocks Wifi access to targeted device
- zANTI
- Spoof MAC
- Create Malicious Wifi Hotspot
- Scan for open ports
- Exploit Router Vulnerabilities
- Password complexity audits
- Man-in-Middle attack
- DoS attaack
- Network Spoofer - Change websites on other peoples computers
- Low Orbit Ion Cannon - Perform DoS and DDoS attacks
- DroidSheep - Perform web session hijacking
- Orbot - Proxy app that hides identity
- FaceNiff - Sniff and intercept web session profiles
- Android Trojans
- BankBot
- SpyDealer
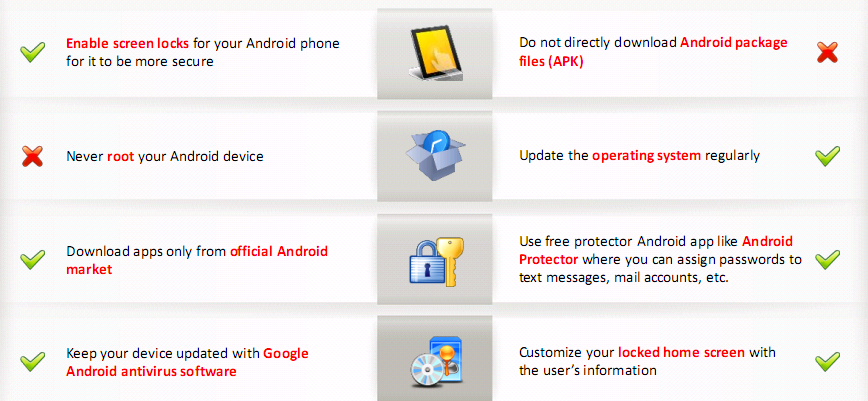
Securing Android Devices
Hacking IOS
- Apple IOS
- Apples Mobile OS
- Uses direct manipulation and multi touch gestures

- Jailbreaking
- Installing a modified set of kernel patches that allows users to run third party applications not singed by OS vendor
- Provides root access to the OS
- Removes sandbox restrictions
- Types of Jailbreaking
- Userland Exploit - Allows user-level access
- iBoot Exploit - Allows user-level access and iboot-level access
- Bootrom Exploit - Allows user-level access and iboot-level access
- Jailbreaking Techniques
- Untethered Jailbreaking - Allows the device to reboot and the kernel will still be patched
- Semi-tethered Jailbreaking - If the device reboots the kernel will no longer have a patched kernel but will still be usable for normal functions
- Tethered Jailbreaking - If the device reboots the kernel will no longer have a patched kernel and will get stuck in a partially started state
- Jailbreaking Tools
- Cydia - Enables a user to find and install software packages
- Pangu Anzhuang - Online jailbraking app
- Keen Jailbreak - Unofficial semi-tethered tool
- IOS Trojans
- AceDeceiver - Exploits flaw in DRM (Digitals Rights Management)
- Spy/MobileSpy!iPhoneOS - Malware allows and attacker to eavesdrop all incoming and outgoing communications
Securing IOS Devices

Mobile Device Management (MDM)
- Mobile Device Management
- Over-the-air or wired distribution of applications and configurations
- Helps implementing enterprise-wide policies
- Helps deploy and manage software applications across all enterprise mobile devices
- MDM Solutions
- IBM MaaS360 - Cloud platform
- XenMobile - Citrix enterprise MDM
- Bring Your Own Device (BYOD)
- Refers to a policy allowing an employee to bring their personal devices
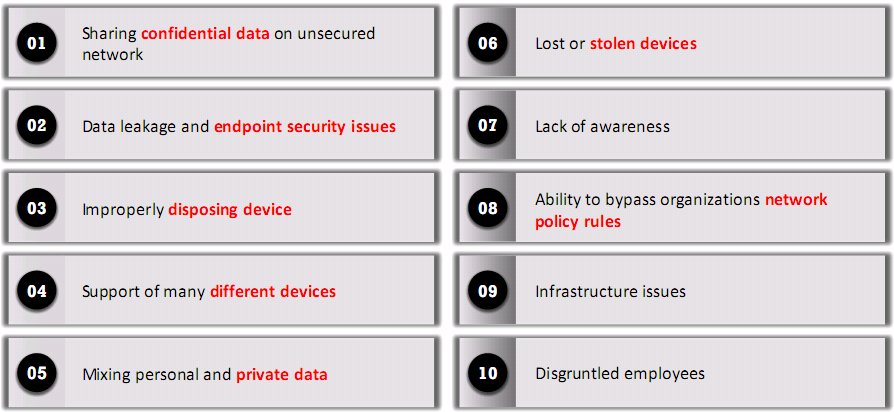
- BYOD Risks
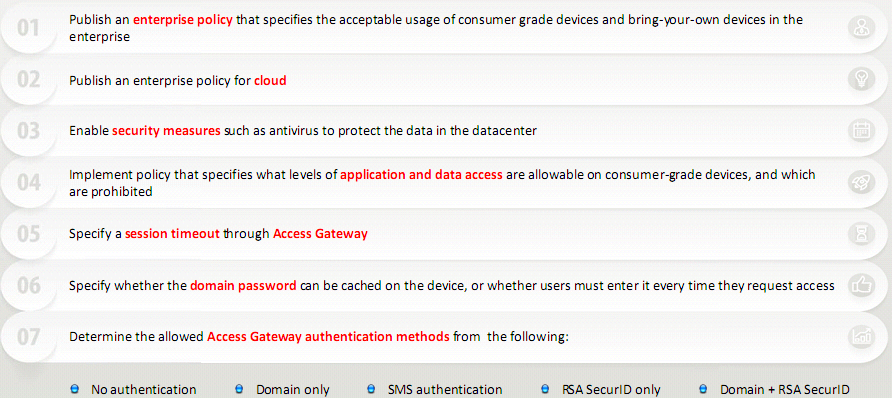
- BYOD Policy Implementation
- Define your requirements
- Select device of your choice and build a tech portfolio
- Develop policies
- Security
- Support
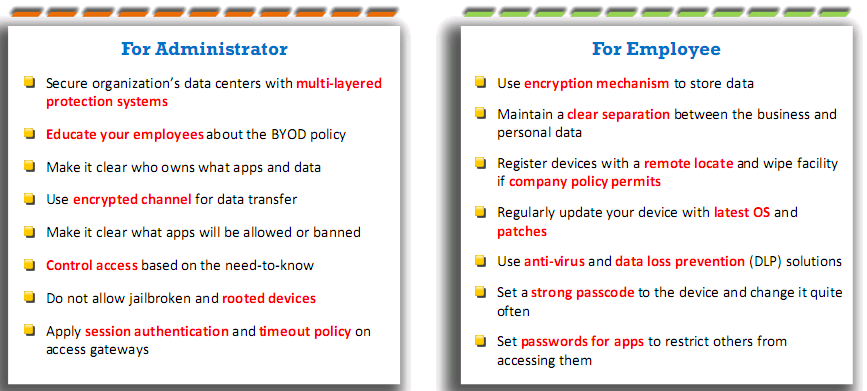
- BYOD Security Guidelines
Mobile Security Guidelines and Tools
General Guidelines for Mobile Platform Security


Mobile Device Security Guidelines for Administrators
SMS Phishing Countermeasures
